Seam tracking sensor iST ARC
Intelligent control for precision weld seams
In robot welding, every weld seam must be precisely positioned. The iST ARC weld seam tracking sensor from ABICOR BINZEL tracks even challenging joint contours, gaps, and tolerances on the component – and adjusts the seam tracking in real time.
Advantages of iST ARC weld seam tracking sensors
With intelligent control, such as a sensor for weld seam tracking, you can avoid rejects or expensive rework right from the start. In addition, such a sensor increases the quality of the weld seams, because even minor deviations on the component are detected immediately and compensated for in real time (adaptive parameter adjustment). Because the iST ARC sensor ensures that the weld seam is positioned correctly, in most cases you can also increase the welding speed and do not have to waste time or material on weld seams that are too large.
The sensors in the iST ARC product family feature a wide range of seam patterns for a variety of different types of seams as standard. The software is highly flexible, allowing you to add your own specific seam patterns if required. This is extremely helpful, as the applications are usually very specialized.
The advantages at a glance:
- Intelligent control easily detects deviations in the workpiece joint from a minimum gap width of 0.1 mm and adjusts the seam tracking in real time
- Reduce your reject rate and rework costs in automated MIG/MAG welding and TIG welding
- Suitable for all common metals such as stainless steel and stainless steel alloys as well as aluminum
- Suitable for various joining processes such as arc welding, laser welding, and submerged arc welding, among others
iST ARC sensor types
ABICOR BINZEL offers three types of sensors for weld seam tracking. All of them have excellent tracking performance. As an intelligent control system, the sensor software of the robot controller can provide information about the seam characteristics such as area, volume, and angle as required, enabling adaptive parameter adjustment.
The iST ARC is available in three versions with different fields of view and resolution:

The iST ARC 15 with a 15 mm horizontal field of view and high resolution is suitable for seam tracking in narrow gaps, especially in thin sheet metal applications.

With its 30 mm horizontal field of view, the iST ARC 30 offers the perfect application solution where field of view and resolution are required.

The iSTR ARC 50 with a 50 mm horizontal field of view is ideal for thick sheet metal welding and multi-layer welding due to its large field of view and high flexibility in seam search algorithms.
How iST ARC sensors work
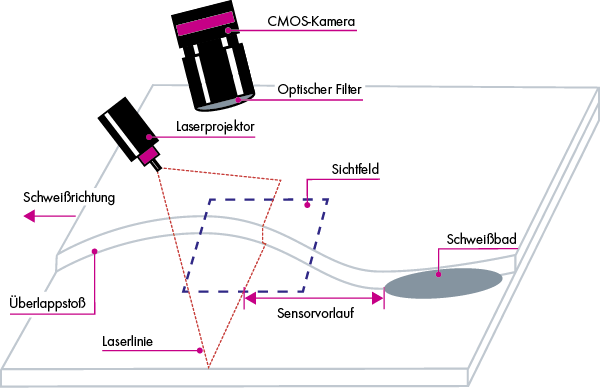
The iST ARC sensors for weld seam tracking are triangulation sensors and operate according to the principle of laser triangulation. This works as follows:
In laser triangulation, the sensor head projects a laser line onto the workpiece, which is refracted by the butt joint. The camera in the sensor then captures the reflected laser line and thus also the refraction of light at the butt joint.
The algorithms of the sensor then analyze the position and shape of the laser line that is refracted at the guided edge/joint in the camera image. In this way, their position and the condition of the seam joint are measured. The robot control system or welding machine receives this information and corrects the welding path and parameters as necessary.
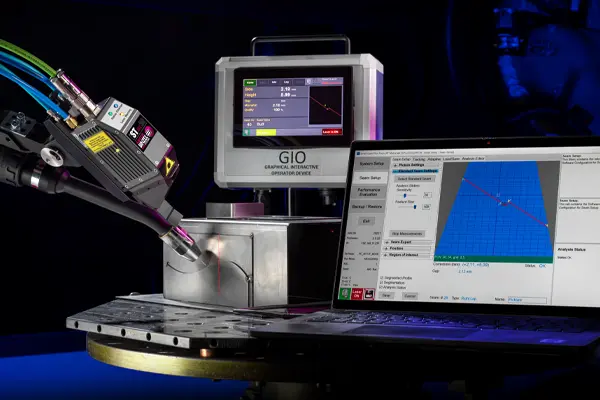

The functions integrated into the iST ARC weld seam sensors, such as automatic gain control, graphical interactive operator device (GIO), and offline recording, greatly simplify system setup and operation. In addition, maintenance-friendly protective glasses minimize downtime.
This means in detail:
Image processing in the sensor head
The complete image processing system of the iST ARC seam tracking sensors is integrated into the sensor head. This solution eliminates the need for a process computer and saves space in the robot cell. Another advantage is that the interface or communication between the iST ARC sensor head and the robot – the breakout board – can be easily installed in the control cabinet. Furthermore, the lower weight has an additional positive effect on the volume of the delivery and thus on freight costs.
One cable for power supply & data
The power supply to the sensor head and the data connection to and from the sensor head to the breakout board are provided by a single connection cable. This reduces the number of additional interfaces and thus further sources of error in your automated applications.
Easy operation with the graphical interactive operator display (GIO)
An interesting and practical assistance system for the iST ARC is the optional graphical interactive operator display (GIO). With this compact and robust unit, operators or maintenance technicians can see exactly what the system is doing and, if necessary, record it for later analysis. It is not necessary to stop the welding cell in order to connect the laptop computer.
Automatic adaptive parameter adjustment
The automatic gain control of the iST ARC weld seam tracking sensors automatically adjusts the camera shutter speed, laser intensity, and other parameters. For example, if there is overexposure, the laser intensity is automatically reduced. This feature makes it easier to set up the seam parameters and prevents suboptimal parameterization.
Easy maintenance/repair
The design of the sensor head on all iST ARC weld seam sensors allows for easy maintenance. This includes, for example, the ability to replace the protective glass yourself.
In the event of a malfunction that cannot be rectified by you, please contact your local ABICOR BINZEL representative. In most cases, malfunctions can be rectified remotely, which means that you do not need to send in the sensor. If it is necessary to send in the sensor, a replacement sensor can be adapted quickly, easily, and precisely using the dovetail mounting plate.




Offline optimization for service questions
SIf you have any questions about how to improve the performance of your iST ARC sensor in your specific application, take advantage of the quick and easy offline optimization option. Simply send us the recorded weld seam information from your automated applications directly by email to: seam-tracking@binzel-abicor.com ? We will check the data, optimize it, and return the optimized parameter set to you. This minimizes long downtimes for your seam tracking sensor and time-consuming and expensive on-site visits.
Service/contact
Do you need advice over the phone, a personal consultation on site, or direct contact with a distributor? Please contact us directly by e-mail at: seam-tracking@binzel-abicor.com .
FAQs about weld seam tracking
What can happen during robotic welding?
Everyone is familiar with this situation: the components are checked by a robot after welding and often weld seams are found in places where they do not actually belong, or they are of poor quality. The cause: poorly clamped or inadequately prepared components from previous production processes. These errors cannot be compensated for in the welding process because the robot follows its programmed path, resulting in rework or, in the worst case, rejects being produced.
How do you prevent weld seam defects?
The simplest solution would be precisely prefabricated components within all tolerances and high-precision clamping fixtures. However, this is virtually impossible or often not economically viable. With machine or robot-controlled welding, you can keep the welding torch correctly positioned with the help of a weld seam tracking sensor. The sensor provides the welding robot with data on the actual position of the joint to be welded and welding takes place exactly there. Thermal distortion during the welding process or deviations from component preparation are compensated for. The weld seam size can also be measured, allowing the robot controller to adapt the welding process.
Which welds must weld seam tracking systems be able to track?
In sheet metal welding, optical weld seam tracking systems must be able to recognize and track different types of joints. These include:
- Butt joint
- Fillet weld
- Lap joint
- Edge weld
- External seam
- Strong external seam
- Multi-pass welding for wide weld joints

